WHAT IS NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION?
Non-verbal communication refers to all communication that occurs without the use of words spoken or written. Non-verbal communication is concerned with body movements (kinesics), space (proxemics), chronemics (time) and vocal (paralinguistic) features. It includes all unwritten and unspoken messages, both intentional and unintentional.
Personal appearances, facial expressions, postures, gestures, eye contact, voice proximity, and touch are all non-verbal signals that influence the way in which a message is interpreted and understood.
Kinesics is the study of the body's physical movements. It is the way the body communicates without words, i.e., through the various movements of its parts.
Personal appearance play an important role in communication because people see before they hear. Appearance includes clothes, hair, accessories, cosmetics and so on.
Posture comes under Kinesics. Posture generally refers to the way we hold ourselves when we stand, sit or walk.
1. Slumped posture = low spirit
2. Erect posture = high spirits, energy and confidence
3. Lean forward = open, honest, and interested
4. Lean backward = defensive or disinterested
5. Crossed arms = defensive and not ready to listen
6. Uncrossed arms = willingness to listen
Gesture is the movement made by hands, head, or face. Skillful and appropriate gestures can add to the impact of verbal communication.
Facial Expression plays an important part in non-verbal communication.
The face is the most expressive part of our body. A smile stands for friendliness, a frown for discontent, raised eyebrows for disbelief, tightened jaw muscles for antagonism, etc.
Eye contact Eyes are considered to be the windows of the soul. Eye contact is a direct and powerful form of non-verbal communication. Eyes are also a rich source of feed back.
2. Proxemics [study of physical space]
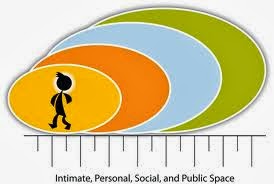
Proxemics is the study of physical space in interpersonal relations. Space is related to behavioural norms. The way people use space communicates a lot. In a professional setting, space is used to signal power and status. For instance, the head of a company has a larger office than junior employees.
Like kinesics, proxemics also has cultural variations. Edward T. Hall (1996) divides space into four distinct zones.
a) Intimate Zone starts with personal touch and extends just to 18 inches (one and half feet). Members of the family, lovers, spouses, relatives, and parents fall in this zone. The best example is the mother child relationship.
b) Personal Zone stretches from 18 inches (one and a half feet) to 4 feet. Close friends, colleagues, peers, etc. fall in this zone.
c) Social Zone Social events take place in the radius of 4 feet to 12 feet. In this zone relationships are more formal and official. People are more cautious in their movements.
d) Public Zone starts from 12 feet and may extend to 25 feet or to the range of eyesight and hearing. Events that take place in this zone are formal. Here the audience views what is happening as an impartial observer. The degree of detachment is very high. Public figures like the prime minister of a country, for example, have to maintain this distance for security reasons.
3. Chronemics [use of time]
Chronemics is the study of how human beings communicate through their use of time. In the professional world, time is a valuable resource. If we are late for an appointment, people react negatively. If early, we are considered either over eager or aggressive. So one must be on time. By valuing someone else's time, we communicate our professionalism or seriousness both subtly and explicitly.
=================================================================
Personal appearance play an important role in communication because people see before they hear. Appearance includes clothes, hair, accessories, cosmetics and so on.
Posture comes under Kinesics. Posture generally refers to the way we hold ourselves when we stand, sit or walk.
1. Slumped posture = low spirit
2. Erect posture = high spirits, energy and confidence
3. Lean forward = open, honest, and interested
4. Lean backward = defensive or disinterested
5. Crossed arms = defensive and not ready to listen
6. Uncrossed arms = willingness to listen
Gesture is the movement made by hands, head, or face. Skillful and appropriate gestures can add to the impact of verbal communication.
Facial Expression plays an important part in non-verbal communication.
The face is the most expressive part of our body. A smile stands for friendliness, a frown for discontent, raised eyebrows for disbelief, tightened jaw muscles for antagonism, etc.
Eye contact Eyes are considered to be the windows of the soul. Eye contact is a direct and powerful form of non-verbal communication. Eyes are also a rich source of feed back.
2. Proxemics [study of physical space]
Proxemics is the study of physical space in interpersonal relations. Space is related to behavioural norms. The way people use space communicates a lot. In a professional setting, space is used to signal power and status. For instance, the head of a company has a larger office than junior employees.
Like kinesics, proxemics also has cultural variations. Edward T. Hall (1996) divides space into four distinct zones.
a) Intimate Zone starts with personal touch and extends just to 18 inches (one and half feet). Members of the family, lovers, spouses, relatives, and parents fall in this zone. The best example is the mother child relationship.
b) Personal Zone stretches from 18 inches (one and a half feet) to 4 feet. Close friends, colleagues, peers, etc. fall in this zone.
c) Social Zone Social events take place in the radius of 4 feet to 12 feet. In this zone relationships are more formal and official. People are more cautious in their movements.
d) Public Zone starts from 12 feet and may extend to 25 feet or to the range of eyesight and hearing. Events that take place in this zone are formal. Here the audience views what is happening as an impartial observer. The degree of detachment is very high. Public figures like the prime minister of a country, for example, have to maintain this distance for security reasons.
3. Chronemics [use of time]
Chronemics is the study of how human beings communicate through their use of time. In the professional world, time is a valuable resource. If we are late for an appointment, people react negatively. If early, we are considered either over eager or aggressive. So one must be on time. By valuing someone else's time, we communicate our professionalism or seriousness both subtly and explicitly.
=================================================================
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)